Elderberry has recently gained popularity as a natural remedy, but it has a long-standing history in traditional medicine. Known for its immune-boosting properties and rich nutrient profile, elderberry (Sambucus) is one of nature’s most powerful berries. In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about elderberries, their benefits, uses, potential side effects, and how they can enhance your overall health.
What Is Elderberry?
Elderberry refers to the fruit produced by various species of the Sambucus tree. The most commonly used variety in medicine is Sambucus nigra, also known as European elderberry or black elderberry. The tree is native to Europe but can now be found in parts of North America, Asia, and Northern Africa.
They are small, dark purple berries that grow in clusters. While the raw berries, bark, and leaves are toxic when consumed in large quantities, proper preparation—like cooking—neutralizes these toxic substances, making the berries safe and beneficial for consumption.
Did you know?
The elderberry market was valued at approximately $429 million in 2021 and is expected to reach $650 million by 2027. n the U.S., elderberry became the second most popular herbal supplement in 2020, with annual sales exceeding $275 million. Europe remains one of the largest markets for elderberry, particularly in countries like Germany and Austria, where elderberry syrups and extracts are commonly used in traditional medicine.

A Brief History
Elderberry has a rich history dating back to ancient times. The Greek physician Hippocrates, often referred to as the “Father of Medicine,” called the elder tree his “medicine chest” due to its wide range of healing properties. Indigenous peoples and ancient civilizations used various parts of the elderberry plant to treat ailments such as fever, rheumatism, and burns. Today, it continues to be a staple in folk medicine across Europe and North America.
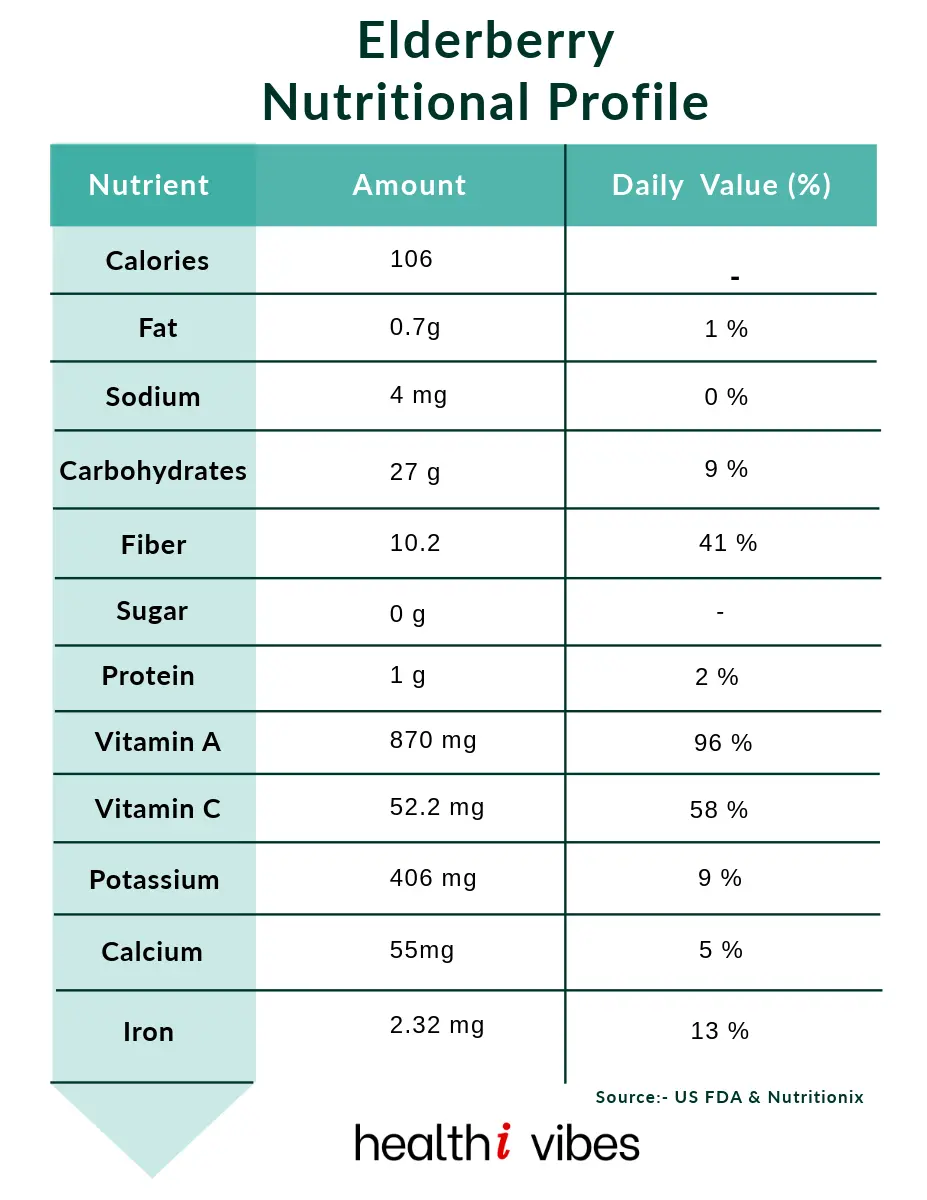
Nutritional Profile and Active Components of Elderberry
Elderberries (Sambucus nigra) are packed with bioactive compounds that contribute to their health benefits. These include:
- Anthocyanins: These are potent antioxidants responsible for the deep purple color of elderberries. Anthocyanins have anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties.
- Flavonoids: Including Rutin, quercetin and kaempferol, these compounds have antioxidant effects, helping to protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Vitamin C: The berries are rich in vitamin C, an essential nutrient that supports immune function and skin health.
- Phenolic Acids: These acids act as antioxidants and contribute to overall health by neutralizing free radicals.
- Fiber: Elderberries contain dietary fiber, which supports digestive health and helps in maintaining a healthy gut.
- Trace Minerals: These berries are a source of iron, potassium, and copper, all of which are important for various bodily functions.
Health Benefits of Elderberry
Boosts Immune System: Elderberry is widely recognized for its ability to enhance immune function. The anthocyanins in elderberry increase the production of cytokines, which are proteins that help regulate immune responses, making it a popular remedy for colds and flu. Studies suggest that elderberry can reduce the duration and severity of cold and flu symptoms when taken early.
Rich in Antioxidants: The high levels of antioxidants in elderberries help fight free radicals, which are unstable molecules that contribute to aging and diseases like cancer. Antioxidants neutralize these molecules, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Supports Heart Health: The fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins in elderberries may promote heart health by reducing cholesterol levels, improving circulation, and lowering blood pressure. The high potassium content can help regulate blood pressure, while the fiber helps manage cholesterol.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Elderberry’s anthocyanins and flavonoids have anti-inflammatory effects that may alleviate symptoms of conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and allergies by reducing inflammation.
Promotes Digestive Health: Due to its fiber content, elderberry can aid digestion, promote regular bowel movements, and support a healthy gut microbiome.
Improves Skin Health: The antioxidants and vitamin C in elderberry support skin health by boosting collagen production and fighting oxidative stress, which contributes to premature aging.
Active Components in Elderberry
Elderberries (Sambucus nigra) contains bioactive compounds that contribute to their health benefits. These include:
- Anthocyanins: These are potent antioxidants responsible for the deep purple color of elderberries. Anthocyanins have anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating properties.
- Flavonoids: Including quercetin and kaempferol, these compounds have antioxidant effects, helping to protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Vitamin C: Elderberries are rich in vitamin C, an essential nutrient that supports immune function and skin health.
- Phenolic Acids: These acids act as antioxidants and contribute to overall health by neutralizing free radicals.
- Fiber: Elderberries contain dietary fiber, which supports digestive health and helps in maintaining a healthy gut.
- Trace Minerals: These berries are a source of iron, potassium, and copper, all of which are important for various bodily functions.
Contraindications and Who Should Avoid Elderberry
While elderberry is generally safe for most people when consumed in moderation, certain individuals should exercise caution:
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women: There is limited research on the safety of elderberry during pregnancy and breastfeeding. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before using elderberry supplements in these situations.
Autoimmune Conditions: Elderberry stimulates the immune system, which may be problematic for individuals with autoimmune conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or multiple sclerosis. Overstimulation of the immune system in these individuals could worsen symptoms.
Surgery Patients: Due to its immune-modulating effects, elderberry may interact with immune responses during or after surgery. It’s recommended to stop using elderberry at least two weeks before surgery.
Allergies: People with allergies to plants in the Adoxaceae family, which includes elderberry, should avoid it as it may trigger allergic reactions.
Precautions
Elderberry Toxins: Consuming raw elderberries, leaves, or bark can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea due to the presence of cyanogenic glycosides, which are toxic compounds that can release cyanide. Cooking or processing elderberries helps remove these toxins.
Drug Interactions: Elderberry may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect the immune system or blood clotting. Consult with a healthcare provider before using it if you are taking any medications.
Excessive Consumption: While it is generally safe, excessive consumption may lead to side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Children: The safety of elderberry in children has not been fully established. Consult with a pediatrician before giving it to children.
Hypoglycemia: It may lower blood sugar levels, so people with diabetes or those on medication to regulate blood sugar should monitor their blood glucose levels carefully when using elderberry products.
Read about: Milk Thistle- Nature’s Liver Protector
Dosage Forms of Elderberry
Commercial Elderberry is available in several dosage forms, including:
Syrups: One of the most popular forms, often used to treat cold and flu symptoms.
Capsules and Tablets: These contain concentrated elderberry extract and are convenient for daily use.
Teas: Elderberry tea offers a soothing way to enjoy the benefits, particularly during cold seasons.
Gummies: A popular choice for children or those who prefer a sweeter, more palatable option.
Conclusion
Elderberry stands out as a powerful natural remedy with a rich history of use in traditional medicine. It is especially beneficial for boosting immune health and fighting cold and flu symptoms. Packed with vitamins, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds, elderberries offer a variety of health benefits that can support your overall wellbeing. Whether you choose syrup, tea, or supplements, incorporating this superfood into your routine can be a simple and natural way to enhance your health.
However, it’s essential to use the products responsibly. Always consult a healthcare professional if you have any underlying conditions or are pregnant. With the right approach, elderberries can be a valuable addition to your health and wellness journey.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. While it has been used traditionally for various health benefits and supported by some scientific research, individual results may vary. The content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement. Especially if you have underlying health conditions, are pregnant, breastfeeding, or are taking medications. The use of elderberry products should be done with care, and raw elderberries should never be consumed without proper preparation.
The above article contains affiliate links. We may earn a commission if you choose to buy after clicking the link