Have you ever heard of artichoke leaf benefits? While it might not be as familiar as other herbs, it has been gaining attention for its potential health benefits, especially when it comes to liver health.
Artichoke leaf (Cynara scolymus) has been valued for centuries, not just as a food but also for its health benefits. It’s especially known for supporting liver health along with high value of nutrients.
In this article, we’ll explore the history of artichoke leaf, its benefits backed by science, possible side effects, and its key role in liver health.
A Brief History
The artichoke, scientifically known as Cynara scolymus, is native to the Mediterranean region. Its cultivation dates back to ancient times, with records indicating its use in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome. The plant was highly valued not only for its edible parts but also for its medicinal properties. The Egyptians used it to aid digestion and support the liver, while the Greeks and Romans considered it a medicinal food. Over the centuries, artichokes spread across Europe and eventually made their way to the Americas, where they continue to be a popular vegetable.
Nutritional Profile
Artichoke leaves, while often consumed as an extract or supplement, contain a variety of nutrients and bioactive compounds that contribute to their health benefits. Below is a list of the key components typically found in artichoke leaves:
Vitamins:
- Vitamin C: Known for its antioxidant properties, it supports immune function and helps combat oxidative stress.
- Vitamin K: Important for blood clotting and bone health.
- Folate (Vitamin B9): Crucial for cell division and proper brain function.
- Vitamin B6: Supports brain health, mood regulation, and red blood cell production.
- Minerals:
- Magnesium: Helps with muscle function, energy production, and maintaining bone density.
- Potassium: Essential for heart function, fluid balance, and nerve signals.
- Calcium: Important for bone health and muscle function.
- Phosphorus: Supports bone health and energy storage.
- Fiber:
- Artichoke leaves are rich in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion, helps lower cholesterol, and supports gut health.
- Bioactive Compounds:
- Cynarin: A compound that stimulates bile production and supports liver detoxification.
- Chlorogenic Acid: An antioxidant that helps lower blood pressure and may improve glucose metabolism.
- Luteolin: A flavonoid with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
- Silymarin: A compound known for its liver-protective effects, often found in artichokes and milk thistle.
- Antioxidants:
- Quercetin: An antioxidant that helps reduce inflammation and supports heart health.
- Rutin: Known for its role in strengthening blood vessels and reducing oxidative stress.
- Caffeic Acid: An antioxidant with potential anti-cancer properties.
Scientific Benefits of Artichoke Leaf
Liver Health and Detoxification
Artichoke leaf is famous for supporting liver health. The plant contains cynarin and luteolin, compounds that boost bile production. Bile helps digest fats and flush toxins from the body. Research shows that artichoke leaf can protect the liver from damage and may even help it regenerate. This makes it useful for treating fatty liver disease and other liver problems.
Cholesterol Regulation
Artichoke leaf also helps manage cholesterol levels. Studies show that it can reduce both total cholesterol and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol. This effect is likely due to its ability to increase bile, which helps break down cholesterol more efficiently.
Digestive Health
Artichoke leaf has long been used to ease digestion. Its main compound, cynarin, boosts bile flow, which improves fat digestion. It has also been found to relieve bloating, indigestion, and symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties
Artichoke leaves are rich in antioxidants like quercetin, rutin, and caffeic acid. These antioxidants fight free radicals, reducing oxidative stress, which can lead to diseases like heart disease and cancer. Artichoke’s anti-inflammatory effects may also help reduce inflammation in the body, including in cases of arthritis.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Research suggests that artichoke leaf can help control blood sugar levels. Some studies show it improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood glucose, making it helpful for people with diabetes or those at risk of the condition.
Contraindications of Artichoke Leaf
While artichoke leaf benefits are important, certain individuals should exercise caution due to potential contraindications. Below is a detailed look at the contraindications of artichoke leaf, along with scientific evidence that support these concerns.
1. Allergies to Asteraceae/Compositae Family
Artichoke belongs to the Asteraceae family, which includes plants like daisies, marigolds, and chrysanthemums. People allergic to plants in this family may also be allergic to artichoke leaf. Symptoms of an allergic reaction could include:
- Skin rashes
- Itching
- Hives
- Swelling
- Respiratory difficulties (in severe cases)
Scientific Reference: Occupational rhinitis and bronchial asthma has been reported in vegetable warehouse workers after sensitization to artichoke.
2. Bile Duct Obstruction or Gallstones
Artichoke leaf stimulates bile production, which aids in digestion. While this is beneficial for most people, it can pose risks for individuals with bile duct obstruction or gallstones. Increased bile flow in people with gallstones can lead to blockages or exacerbate existing obstructions, causing pain or complications. Symptoms of gallstone issues may include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Scientific Reference: Mount Sinai- Gall Bladder Stones
3. Cholecystitis (Inflamed Gallbladder)
Artichoke leaf is not recommended for people with cholecystitis, or inflammation of the gallbladder, due to its bile-stimulating effects. By promoting bile secretion, it could worsen inflammation in the gallbladder or cause further complications.
Scientific Reference: Mount Sinai- Gall Bladder Stones
4. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
There is limited scientific data on the safety of artichoke leaf during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The lack of research means there are no well-documented effects, either positive or negative, on fetal development or infant health. Therefore, many health professionals advise against using artichoke leaf supplements during pregnancy or breastfeeding unless specifically prescribed by a healthcare provider.
5. People with Low Blood Pressure
Artichoke leaf may have blood pressure-lowering effects due to its vasodilatory and diuretic properties. While this is beneficial for people with hypertension, it may pose a risk for those who already have low blood pressure (hypotension). Consuming artichoke leaf could lead to dangerously low blood pressure, causing dizziness, fainting, and weakness.
Scientific Reference: Effects of artichoke on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis
6. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Gastrointestinal Sensitivity
Although artichoke leaf is used to alleviate digestive issues, it can, in some cases, cause gastrointestinal discomfort, particularly for people with sensitive stomachs or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Common side effects may include:
- Bloating
- Gas
- Diarrhea or loose stools
These side effects are usually dose-dependent and more common with higher intakes of artichoke leaf extract.
Scientific Reference: Artichoke Leaf in IBS
7. Interaction with Medications
Artichoke leaf can interact with certain medications, including:
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins): Since artichoke leaf can lower cholesterol naturally, it may enhance the effects of statin medications, leading to excessively low cholesterol levels. (Reference)
- Antihypertensive medications: Artichoke leaf may increase the effects of medications used to lower blood pressure, potentially causing hypotension. (reference)
- Diuretics: Artichoke leaf has mild diuretic properties, which could amplify the effects of diuretic medications, leading to dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
Scientific Reference:
- A pharmacological review in Phytomedicine indicated potential interactions between artichoke leaf extract and cholesterol or blood pressure medications .

Common Dosage Forms of Artichoke Leaf Extract and Their Benefits
Artichoke leaf extract is available in various dosage forms to suit different preferences, treatment needs, and absorption methods. Here’s a list of the most common forms of artichoke leaf extract and why they are used:
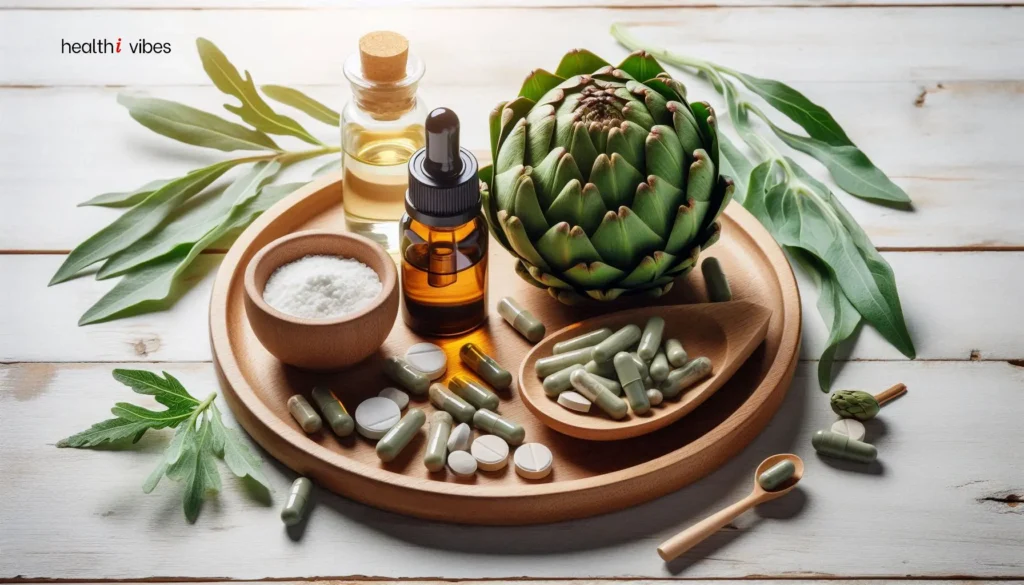

1. Capsules and Tablets
- Why: Capsules and tablets are one of the most common forms of artichoke leaf extract due to their convenience and precise dosing. They are easy to take, provide consistent dosage, and are portable.
- Benefits:
- Precise measurement of the active compounds like cynarin and luteolin.
- Ideal for long-term use as they are stable and have a long shelf life.
- Easy to include in daily supplement routines.
2. Tinctures (Liquid Extract)
- Why: Tinctures are a liquid form of artichoke leaf extract, usually alcohol- or glycerin-based. This format allows for quicker absorption into the bloodstream, making it beneficial for people who prefer not to swallow pills or need faster effects.
- Benefits:
- Rapid absorption compared to capsules or tablets.
- Flexible dosing, as it allows users to adjust the amount taken easily.
- Can be mixed with water or other beverages for easier consumption.
3. Tea (Infusion)
- Why: Artichoke leaf tea is a traditional way of consuming the herb. It involves steeping dried leaves in hot water, which extracts its beneficial compounds.
- Benefits:
- Provides a soothing effect, making it a good option for digestive issues.
- Contains antioxidants and bioactive compounds in a mild form.
- Promotes relaxation and may stimulate digestion when consumed after meals.
4. Powdered Extract
- Why: Powdered artichoke leaf extract can be mixed into smoothies, juices, or water. It provides a more flexible way to incorporate artichoke extract into the diet without having to take pills.
- Benefits:
- Versatile and can be added to food or drinks.
- Offers a concentrated dose of artichoke leaf’s active compounds.
- Suitable for those who prefer a more natural, unprocessed form of the extract.
5. Softgels
- Why: Softgel capsules contain liquid artichoke leaf extract in a gelatin-based shell, making them easier to swallow and sometimes faster to absorb than tablets or capsules.
- Benefits:
- Easier to swallow for people who have difficulty with tablets.
- Encapsulated liquid allows for faster absorption in the body.
- Softgels are often more stable and preserve the active ingredients better than powders.
6. Standardized Extract
- Why: Standardized artichoke leaf extract products ensure a specific concentration of active ingredients like cynarin and luteolin, ensuring consistent therapeutic effects. These extracts are often available in capsules, tablets, or tincture forms.
- Benefits:
- Guarantees a reliable dose of key active compounds for therapeutic use.
- Useful in clinical settings and for individuals seeking specific health benefits, such as liver support or cholesterol management.
Conclusion
Artichoke leaf extract has a rich history of medicinal use, particularly for supporting liver health, aiding digestion, and regulating cholesterol levels. Its powerful bioactive compounds, such as cynarin and luteolin, make it a versatile supplement for promoting overall well-being. Whether in the form of capsules, tinctures, tea, or powder, artichoke leaf extract can be easily incorporated into daily routines to harness its numerous health benefits. However, it’s essential to consider individual needs, potential contraindications, and consult with a healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective use.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is intended for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this blog. Use of herbal supplements like artichoke leaf extract should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions, allergies, or those taking medications.